Difference between revisions of "V2/Concepts/Expression"
| (38 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<h1 class="main-heading">Expression</h1> | <h1 class="main-heading">Expression</h1> | ||
| − | User can make use of Senfi's flexible autonomous | + | User can make use of Senfi's flexible autonomous workflow engine to be alerted of abnormality in the system they are monitoring. |
| − | |||
As introduced, an '''Expression''' is a tool that you can use to monitor your assets and be notified of abnormal situations or events. You can configure an expression to trigger an event to send email or notify your operators in the Digital Twin. Examples of use cases include: a fire is detected in a building, a lift has broken down, or when a machine is overdue for maintenance. Expression editor is the tool you can use to configure these conditions. | As introduced, an '''Expression''' is a tool that you can use to monitor your assets and be notified of abnormal situations or events. You can configure an expression to trigger an event to send email or notify your operators in the Digital Twin. Examples of use cases include: a fire is detected in a building, a lift has broken down, or when a machine is overdue for maintenance. Expression editor is the tool you can use to configure these conditions. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
'''Inputs''' are evaluated by '''Conditions''' to generate a single '''Result'''. | '''Inputs''' are evaluated by '''Conditions''' to generate a single '''Result'''. | ||
| − | When value of '''Result''' changes (from False to True or True to False), an '''Event''' can be triggered. '''Actions''' defined in the Event such as | + | When value of '''Result''' changes (from False to True or True to False), an '''Event''' can be triggered. '''Actions''' defined in the Event such as notifications and commands, are executed when the Event is triggered. |
'''Expression execution type''' allows you to configure how the Expression is executed. e.g: how often the '''Expression''' is evaluated, whether it's immediate or on poll. | '''Expression execution type''' allows you to configure how the Expression is executed. e.g: how often the '''Expression''' is evaluated, whether it's immediate or on poll. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
| − | Using our Smart Weighing Scale measurement from earlier, we can form one simple | + | Using our Smart Weighing Scale measurement from earlier, we can form one simple Expression as follows: |
* Input: <tt>iot_weighingscale_v1.battery_level</tt> | * Input: <tt>iot_weighingscale_v1.battery_level</tt> | ||
* Condition: < 20 | * Condition: < 20 | ||
| − | * Event: '' | + | * Event: ''Battery level low'' |
| − | * Expression execution | + | * Event action: ''Send email notification to remind changing of battery'' |
| + | * Expression execution type: Immediate (means evaluate this rule whenever there is any incoming measurement) | ||
| − | == Inputs, Conditions and Result == | + | == Inputs, Conditions and Result == |
| − | + | Before adding an Expression, you should already have an Event or situation that you wish to be notified about. The Event or situation should be one that can be detected by monitoring data received by Senfi. | |
| − | Before adding | ||
| − | + | [[File:Concepts_Automation_Expression.png|800px|center|link=]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Select [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Asset|'''Assets''']] as '''Inputs''', from which the '''Measurements''', [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Metric|'''Metrics''']], [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Location|'''Location''']] and [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Attribute|'''Attribute''']] can be used to detect an Event or situation. Then, [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression|construct the set of '''Conditions''']] from [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Data_Transformation|data transformation]] or [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Logic|logic]] functions. The set of Conditions will evaluate from false to true or true to false when Event or situation occurs. The result of said '''Conditions''' is the [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Result|'''Result''']] of the Expression. Whenever '''Result''' changes (from true to false and vice versa), [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node#Event|'''Events''']] may be triggered. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Expression Execution Options == | |
| − | + | By setting '''Type''' to '''Immediate''' or '''Polling''', you can choose to execute an Expression when new values are received for any Input Measurements, or periodically, regardless of whether any Input Measurements have changed. | |
| − | + | If Expression is set to run periodically ('''Polling'''), you must specify how often the Expression is executed by setting '''Intervals''' in seconds. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Expression Editor == | |
| − | + | Expressions are defined using the Expression Editor. The Expression Editor is a graph-based '''Drag & Drop''' editor. [[File:Expression_editor.png|thumb|center|600px|Expression Editor|link=]] | |
| − | + | Arrows '''coming in''' from the '''left''' of a node indicate its '''input''' and those '''going out''' from its '''right''' indicate its '''output'''. [[File:Expression_input_output.png|thumb|center|600px|Input & Output of a Node|link=]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Each Node falls into one of the following categories: | |
| − | + | * Asset Identifier | |
| + | * Input | ||
| + | * Data Transformation | ||
| + | * Logic | ||
| + | * Result | ||
| + | * Event | ||
| − | + | Data '''originates''' from '''Metric''' nodes, is '''transformed''' by '''Data Transformation and/or Logic''' nodes, and eventually '''consumed''' by '''Result & Event''' nodes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
;'''Input''' nodes | ;'''Input''' nodes | ||
:'''Metric''' - outputs the value/s of a metric. can be set to output the last known value, or a range of historical values | :'''Metric''' - outputs the value/s of a metric. can be set to output the last known value, or a range of historical values | ||
| Line 119: | Line 67: | ||
:'''Function''' - value-wise transformation. Transform each value, e.g ABS, Floor, Round etc. Can be used after a Metric node and before a Compare node. Outputs the same number of values as its input. | :'''Function''' - value-wise transformation. Transform each value, e.g ABS, Floor, Round etc. Can be used after a Metric node and before a Compare node. Outputs the same number of values as its input. | ||
;Result node | ;Result node | ||
| − | :'''Result''' - '''Result''' | + | :'''Result''' - '''Result''' node. Specifies the '''Result''' of an '''Expression'''. Result can be False to True or True to False. |
| − | ; | + | ;Event nodes |
| − | :''' | + | :'''Event''' - '''Event''' node. Input must always be from the "Result" node. Can have 0 or more "Event" nodes. Instructs Senfi to do something when '''Result''' changes. Event Input Data is passed on to the related Event. |
| − | === | + | === Expression Nodes === |
| + | Each node contains attributes & options which you can modify. To modify the attributes of a node, click on the node and a window will popup to allow you to configure the node. | ||
| − | + | See [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression/Node|Node Type]] for more information about each Node Type. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === Example === | + | === Example of Expression === |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Concepts_Automation_Expression_Example1.png|center|Example 1|thumb|799px|link=]] |
| − | Example 1: A simple | + | Example 1: A simple Expression detecting when a Lift has tripped (safetyTrip == 1). |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Concepts_Automation_Expression_Example2.png|center|Example 2|thumb|799px|link=]] |
Example 2: Detects when a Lift tripped (safetyTrip == 1), AND passengers are trapped in the Lift (load > 0) | Example 2: Detects when a Lift tripped (safetyTrip == 1), AND passengers are trapped in the Lift (load > 0) | ||
| − | === Working with historical values === | + | === Working with historical values === |
When historical values is required to detect an event, the "Range", "Filter" and "Aggregate" nodes are needed. | When historical values is required to detect an event, the "Range", "Filter" and "Aggregate" nodes are needed. | ||
| − | + | By default, a "Metric" node will output the Last Known value of the metric. To obtain historical values of a metric, select "Range value of" for "Metric" node type. | |
| − | By default, a "Metric" node will output the Last Known value of the metric. To obtain historical values of a metric, | ||
| − | + | The configuration options of the "Range value" type allows you to change the range of historical values to output. E.g: You can configure it to output metric values from 1 hour ago till now, or the last 10 received metric values. | |
| − | The configuration options of the "Range" | ||
| − | |||
After obtaining the list of historical values, you can: | After obtaining the list of historical values, you can: | ||
* Filter the list using the "Filter" node. | * Filter the list using the "Filter" node. | ||
| Line 160: | Line 94: | ||
The "Filter" and "Function" nodes can be nested. | The "Filter" and "Function" nodes can be nested. | ||
| − | + | Finally, the list of historical values must be aggregated using the "Aggregate" node before its output can be used by a "Logic" or "Compare" node. | |
| − | Finally, the list of historical values must be aggregated using the "Aggregate" node before its output can be used by a "Logic" or " | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | === Example using historical values === |
| − | + | [[File:Concepts_Automation_Expression_Example3.png|center|Historical Example 1|thumb|800px|link=]] | |
| + | The example above detects when the average return air temperature for an air-conditioner is more than 21°C for over a minute. | ||
| − | + | === Points to note when working with data === | |
| − | + | * Expression will evaluate using available data, even if data is not available for the full range that was specified. E.g. for an expression to use the average of the past 5 minutes data, if only 1 minute of data is available, then instead of waiting until 5 minutes of past data are available, the 1 minute data is used to evaluate the expression. | |
| + | * The most recently received data may not be used in the range for expression that uses immediate execution type. | ||
| + | * For expression of "immediate" execution type, after the expression is modified, it is not immediately re-evaluated, and is only re-evaluated when new data arrives. | ||
| − | + | ==== What's Next ==== | |
| − | + | ----- | |
| − | * | + | * [[V2/Concepts/Preparing for Expression Creation|What is needed to create an Expression]] |
| − | + | * Start [[V2/CMS_Tutorial/User_Tools/Creating_Content/Automation/Expression|creating your own Expression]] | |
| − | * | + | * Learn about [[V2/Concepts/Event|Event]] |
| − | * | + | * Learn about [[V2/Concepts/Alarm|Alarm]] |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 14:49, 29 November 2022
Contents
Expression
User can make use of Senfi's flexible autonomous workflow engine to be alerted of abnormality in the system they are monitoring.
As introduced, an Expression is a tool that you can use to monitor your assets and be notified of abnormal situations or events. You can configure an expression to trigger an event to send email or notify your operators in the Digital Twin. Examples of use cases include: a fire is detected in a building, a lift has broken down, or when a machine is overdue for maintenance. Expression editor is the tool you can use to configure these conditions.
An Expression in Senfi comprises of:
- Inputs - Assets, Metric & Tag values
- Conditions - Data transformation and/or logic
- Result - False to True / True to False
- Event - Trigger Event when Result changes. e.g. fire detected
- Expression execution type - Configures when a Expression is evaluated
Inputs are evaluated by Conditions to generate a single Result. When value of Result changes (from False to True or True to False), an Event can be triggered. Actions defined in the Event such as notifications and commands, are executed when the Event is triggered. Expression execution type allows you to configure how the Expression is executed. e.g: how often the Expression is evaluated, whether it's immediate or on poll.
Inputs --> Conditions --> Result
Result Changed --> Event --> Actions
Example
Using our Smart Weighing Scale measurement from earlier, we can form one simple Expression as follows:
- Input: iot_weighingscale_v1.battery_level
- Condition: < 20
- Event: Battery level low
- Event action: Send email notification to remind changing of battery
- Expression execution type: Immediate (means evaluate this rule whenever there is any incoming measurement)
Inputs, Conditions and Result
Before adding an Expression, you should already have an Event or situation that you wish to be notified about. The Event or situation should be one that can be detected by monitoring data received by Senfi.
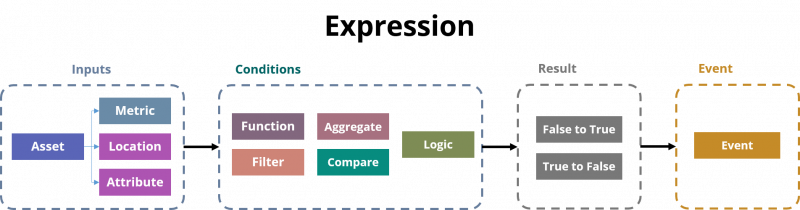
Select Assets as Inputs, from which the Measurements, Metrics, Location and Attribute can be used to detect an Event or situation. Then, construct the set of Conditions from data transformation or logic functions. The set of Conditions will evaluate from false to true or true to false when Event or situation occurs. The result of said Conditions is the Result of the Expression. Whenever Result changes (from true to false and vice versa), Events may be triggered.
Expression Execution Options
By setting Type to Immediate or Polling, you can choose to execute an Expression when new values are received for any Input Measurements, or periodically, regardless of whether any Input Measurements have changed.
If Expression is set to run periodically (Polling), you must specify how often the Expression is executed by setting Intervals in seconds.
Expression Editor
Expressions are defined using the Expression Editor. The Expression Editor is a graph-based Drag & Drop editor.
Arrows coming in from the left of a node indicate its input and those going out from its right indicate its output.
Each Node falls into one of the following categories:
- Asset Identifier
- Input
- Data Transformation
- Logic
- Result
- Event
Data originates from Metric nodes, is transformed by Data Transformation and/or Logic nodes, and eventually consumed by Result & Event nodes.
- Input nodes
- Metric - outputs the value/s of a metric. can be set to output the last known value, or a range of historical values
- Logic Nodes
- Compare - comparison operators. e.g. <, >=, ==, !=
- Logic - perform "AND" or "OR" between 2 or more boolean values
- Data Transformation nodes
- Filter - used to filter a range of values and output a subset number of values. Can only be used after a Metric node in "Range of Value" mode and before an Aggregate
- Aggregate - used to aggregates a range of values into a single value. E.g. sum, average, median. Can only be used after a Metric node in "Range of Value" mode
- Function - value-wise transformation. Transform each value, e.g ABS, Floor, Round etc. Can be used after a Metric node and before a Compare node. Outputs the same number of values as its input.
- Result node
- Result - Result node. Specifies the Result of an Expression. Result can be False to True or True to False.
- Event nodes
- Event - Event node. Input must always be from the "Result" node. Can have 0 or more "Event" nodes. Instructs Senfi to do something when Result changes. Event Input Data is passed on to the related Event.
Expression Nodes
Each node contains attributes & options which you can modify. To modify the attributes of a node, click on the node and a window will popup to allow you to configure the node.
See Node Type for more information about each Node Type.
Example of Expression
Example 1: A simple Expression detecting when a Lift has tripped (safetyTrip == 1).
Example 2: Detects when a Lift tripped (safetyTrip == 1), AND passengers are trapped in the Lift (load > 0)
Working with historical values
When historical values is required to detect an event, the "Range", "Filter" and "Aggregate" nodes are needed.
By default, a "Metric" node will output the Last Known value of the metric. To obtain historical values of a metric, select "Range value of" for "Metric" node type.
The configuration options of the "Range value" type allows you to change the range of historical values to output. E.g: You can configure it to output metric values from 1 hour ago till now, or the last 10 received metric values.
After obtaining the list of historical values, you can:
- Filter the list using the "Filter" node.
- Transform each value in the list using the "Function" node.
The "Filter" and "Function" nodes can be nested.
Finally, the list of historical values must be aggregated using the "Aggregate" node before its output can be used by a "Logic" or "Compare" node.
Example using historical values
The example above detects when the average return air temperature for an air-conditioner is more than 21°C for over a minute.
Points to note when working with data
- Expression will evaluate using available data, even if data is not available for the full range that was specified. E.g. for an expression to use the average of the past 5 minutes data, if only 1 minute of data is available, then instead of waiting until 5 minutes of past data are available, the 1 minute data is used to evaluate the expression.
- The most recently received data may not be used in the range for expression that uses immediate execution type.
- For expression of "immediate" execution type, after the expression is modified, it is not immediately re-evaluated, and is only re-evaluated when new data arrives.
What's Next
- What is needed to create an Expression
- Start creating your own Expression
- Learn about Event
- Learn about Alarm





