Difference between revisions of "Computed measurement/zh-cn"
(Created page with "由于您只是在数据到达时执行转换,因此无需执行任何初始化任务或声明任何全局变量。因此,您可以将初始化函数留空:") |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=== 概述 === | === 概述 === | ||
| − | 如[[Concepts# | + | 如[[Concepts/zh-cn#计算的测量|此处]]所述,计算的测量是从其他数据源生成的一种数据。 |
计算的测量的核心是一个'''计算脚本''',该脚本接受'''输入的度量,执行'''逻辑和计算''',并输出一组'''派生参数'''作为'''计算的度量'''。 | 计算的测量的核心是一个'''计算脚本''',该脚本接受'''输入的度量,执行'''逻辑和计算''',并输出一组'''派生参数'''作为'''计算的度量'''。 | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Senfi computed measurement diag v2 zh-cn.png|计算的测量的概述|link=]] |
要使用计算的测量,您必须: | 要使用计算的测量,您必须: | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== 设计 === | === 设计 === | ||
| − | 在设计计算的测量时,首要做的是确定所需的'''输入'''/'''输出'''数据。计算的测量可以将多个[[Measurement|测量]]指定为输入。这些测量中的参数和标签将可用于负责生成输出的函数。 | + | 在设计计算的测量时,首要做的是确定所需的'''输入'''/'''输出'''数据。计算的测量可以将多个[[Measurement/zh-cn|测量]]指定为输入。这些测量中的参数和标签将可用于负责生成输出的函数。 |
==== 输入测量 ==== | ==== 输入测量 ==== | ||
| − | 以您在[https://ems.senfi.io/cms 内容管理系统] 中的权限所能访问的任何[[Measurement|测量]]都可用作计算测量的输入测量。 | + | 以您在[https://ems.senfi.io/cms 内容管理系统] 中的权限所能访问的任何[[Measurement/zh-cn|测量]]都可用作计算测量的输入测量。 |
您应该只选择您所需并具有参数的测量,作为您派生计算的测量的输入测量。 | 您应该只选择您所需并具有参数的测量,作为您派生计算的测量的输入测量。 | ||
==== 输出测量 ==== | ==== 输出测量 ==== | ||
| − | 您要使用计算的测量创建的任何数据都应打包在输出测量中。输出测量与Senfi中的其他[[Measurement|测量]]具有相同的组成(参数,标签,时间戳)。 | + | 您要使用计算的测量创建的任何数据都应打包在输出测量中。输出测量与Senfi中的其他[[Measurement/zh-cn|测量]]具有相同的组成(参数,标签,时间戳)。 |
设计输出测量参数和标签时,应考虑以下事项: | 设计输出测量参数和标签时,应考虑以下事项: | ||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | 其中<tt>measurement</tt>是输入测量的名称,而<tt>data</tt>是来自输入测量的一个或多个测量数据的列表,并遵循着[[Sending_data_to_Senfi# | + | 其中<tt>measurement</tt>是输入测量的名称,而<tt>data</tt>是来自输入测量的一个或多个测量数据的列表,并遵循着[[Sending_data_to_Senfi/zh-cn#讯息格式|Senfi数据消息的格式]]。 |
从测量<tt>temperature_v1</tt>发送一组测量数据的示例。计算函数的脚本将在测试期间被执行一次: | 从测量<tt>temperature_v1</tt>发送一组测量数据的示例。计算函数的脚本将在测试期间被执行一次: | ||
| Line 292: | Line 292: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | 将所有代码放在一起,完整脚本将类似于: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 345: | Line 345: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== 示例二:电梯移动的总楼层数 ==== |
| − | + | 此示例显示了更复杂的计算测量用法。 | |
| − | + | 假设您有一个会发送楼层位置值的电梯控制器(例如,电梯轿厢位于1楼时,楼层位置值为1;电梯轿厢位于2楼,楼层位置值时为2,等等)。您要使用电梯轿厢位置数据来计算移动的楼层总数。 | |
| − | + | 例如,如果先前报告电梯位于1楼,现在报告电梯位于5楼,则移动的楼层总数为5-1 = 4。如果下一次报告电梯位于第7层,则新移动的总楼层数为(7-5)+ 4 = 6,如此类推。 | |
| − | + | <tt>lift_controller_v1</tt>是您输入的电梯控制器的测量(缩写),其中<tt>lsid</tt>是电梯ID标签,而<tt>position</tt>是电梯轿厢位置数据: | |
{ | { | ||
| Line 362: | Line 362: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | 这是您要输出的计算出的测量值,其中<tt>floorsMoved</tt>是移动的楼层总数的累积。您将保留输入测量的标签,以正确将计算的测量值归因于原始电梯: | |
{ | { | ||
| Line 371: | Line 371: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | 由于您要的是累积随时间推移电梯移动的楼层总数,而不仅仅是按单个测量数据执行计算,您将需为此声明一个全局变量<tt>totalFloorsMoved</tt>: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 377: | Line 377: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | 您的计算函数将跨连续的<tt>lift_controller_v1</tt>输入测量执行计算。您将声明一个全局变量<tt>prevFloors</tt>来存储<tt>floorsMoved</tt>测量的先前值,这样一来,在下一个<tt>lift_controller_v1</tt>输入测量上执行计算函数时,可以执行以下计算: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 383: | Line 383: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | 您还可以使用API函数'''getStoredValue'''和'''setStoredValue'''将累积值存储到持久性存储中。这样,即便Senfi在系统维护时中终止并重新初始化计算的测量,您也不会丢失累积的数据。 | |
| − | + | 例如,要读取先前计算的总移动楼层,请执行以下操作: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 391: | Line 391: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | 因此,完成的初始化函数将是: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 427: | Line 427: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | 现在我们需要编写计算逻辑: | |
| − | * | + | * 在收到新的批次输入测量时,对于每个单独的测量,请计算自上次测量以来移动的楼层的绝对数量:<tt>floors moved = abs(current position - previous position)</tt> |
| − | * | + | * 将移动的绝对楼层数加到移动的累积总数中:<tt>total floors moved += floors moved</tt> |
| − | * | + | * 构造并输出计算的测量值 |
| − | * | + | * 将<tt>current position</tt>存储为<tt>previous position</tt>,以供下一次迭代 |
| − | + | 计算函数为: | |
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 478: | Line 478: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | === | + | === 计算的测量脚本API === |
| − | ==== | + | ==== 输出API函数 ==== |
* '''output''' | * '''output''' | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 495: | Line 495: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== 永久存储API函数 ==== |
* '''setStoredValue''' | * '''setStoredValue''' | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 518: | Line 518: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== 计时API函数 ==== |
* '''setInterval''' | * '''setInterval''' | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="Javascript"> | ||
| Line 555: | Line 555: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== 记录API函数 ==== |
| − | + | 以下函数允许您记录消息,而这些消息将显示在[https://ems.senfi.io/cms 内容管理系统]'''开发者'''选项卡的'''调试器'''中。 | |
* '''console.log''' | * '''console.log''' | ||
| Line 564: | Line 564: | ||
* '''console.debug''' | * '''console.debug''' | ||
| − | <span class="right">[[Sending_data_to_Senfi| | + | <span class="right">[[Sending_data_to_Senfi/zh-cn|下一步:将数据发送到Senfi]]</span> |
Latest revision as of 18:16, 20 November 2019
本页详细介绍计算的测量值。
Contents
概述
如此处所述,计算的测量是从其他数据源生成的一种数据。
计算的测量的核心是一个计算脚本,该脚本接受输入的度量,执行逻辑和计算,并输出一组派生参数作为计算的度量。
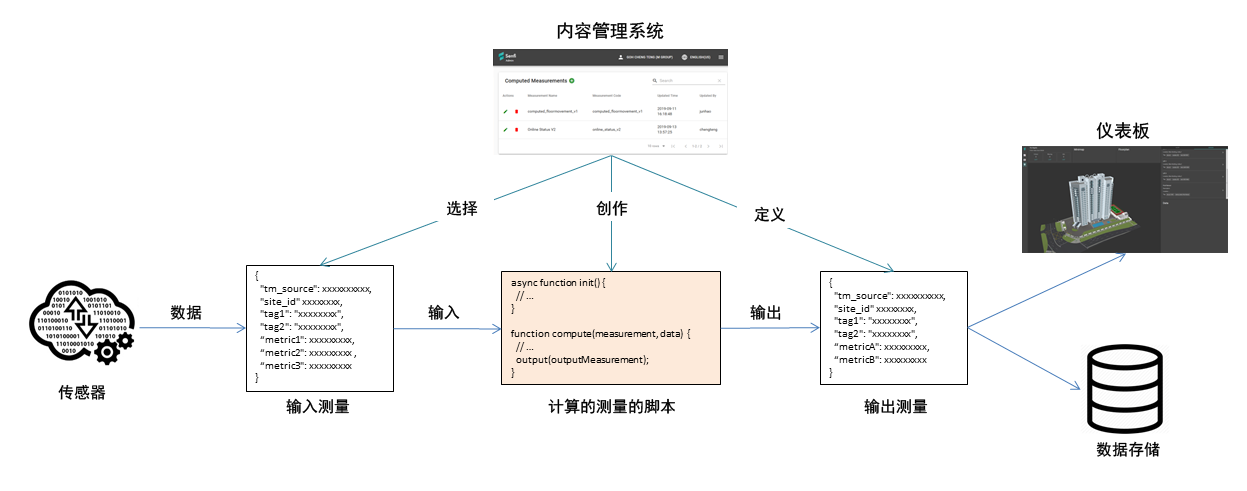
要使用计算的测量,您必须:
- 选择输入测量
- 选择输出参数
- 以输入测量的参数来编写脚本,计算输出参数。
计算的测量的脚本在创建后,将立即初始化,本将一直有效运行,直到删除该计算的测量。每当来自所选输入测量的测量数据到达时,Senfi将执行脚本。
设计
在设计计算的测量时,首要做的是确定所需的输入/输出数据。计算的测量可以将多个测量指定为输入。这些测量中的参数和标签将可用于负责生成输出的函数。
输入测量
以您在内容管理系统 中的权限所能访问的任何测量都可用作计算测量的输入测量。
您应该只选择您所需并具有参数的测量,作为您派生计算的测量的输入测量。
输出测量
您要使用计算的测量创建的任何数据都应打包在输出测量中。输出测量与Senfi中的其他测量具有相同的组成(参数,标签,时间戳)。
设计输出测量参数和标签时,应考虑以下事项:
- 参数:您想要的参数,以及如何根据输入的测量进行计算。
- 标签:哪些标签可让您区分源自不同传感器的计算的测量值。您可以重复使用输入测量中的标签,也可以根据计算出的测量结果来指定不同的标签。
- 时间戳:是使用输入测量的时间戳,还是输出计算的测量的时间。
实施
要生成计算的测量值,您需要编写一个可以处理所选的输入测量值,执行任何必要的计算或逻辑并输出计算出的测量数据的脚本。
JavaScript是用于编写计算的测量脚本的脚本语言。
计算的测量脚本包含两个函数:
- 初始化:设置脚本
- 计算:处理来自输入测量值的数据,执行计算并输出您计算出的测量值
脚本中必须同时包含初始化和计算函数。
init():初始化函数
脚本初始化函数可用于初始化脚本逻辑和状态管理所需的任何数据结构。在创建,修改脚本或系统维护之后重新启动服务,该脚本仅执行一次。
这是初始化函数的脚本模板:
/**
* @name: init
* @description: Perform one-time initialization of your script
* param {string}
**/
async function init() {
// Perform initialization of script here
// TODO
}
如果您在计算的测量不需要跟踪多个或连续输入测量的数据,例如测量值的总和或检查一对输入度量之间的差异,则可以选择将此函数保留为空。
async function init() {
// Initialization not required
}
如果您在计算的测量需要跟踪多个或连续输入测量的数据,则应在此处创建适当的数据结构。
您也可以声明全局变量。 例如:
// Declare global variable for a summation value
let sum;
async function init() {
// Initialize sum to zero
sum = 0;
}
compute():计算函数
每当来自指定输入测量的新测量数据或一批新测量数据到达时,都会执行脚本计算函数。在此函数中,您将从这些输入测量中读取数据,执行所需的任何逻辑或计算,然后输出计算出的测量数据。
这是计算函数的脚本模板:
/**
* @name: compute
* @description: Perform computation on input measurements. This function is called when new measurements arrive
* @param {string} measurement - The input measurement name
* @param {Array.<object>} data - The measurement array data
**/
function compute(measurement, data) {
// Perform calculation on data here
// TODO
// Example output
const outputData = {
metric1: 1,
metric2: true,
metric3: 1,
};
// Output computed measurement. See API docs below
output(outputData);
}
// Output API function
/**
* @function output
* @description: User-invoked function to output a computed measurement
* @param {object} outputData - Object containing output metrics (required tags, optional tags, measurement metrics)
* @param {string} outputData.lsid - [Example] lsid tag (for lifts)
* @param {string} outputData.country - [Example] country tag
* @param {number} outputData.metric1 - [Example] metric1
* @param {boolean} outputData.metric2 - [Example] metric2
* @param {integer} outputData.metric3 - [Example] metric3
**/
请注意,因为使用的数据是测量数据的数组,因此通常您需要遍历输入的数据,才能对每个变量执行计算任务,如下所示:
function compute(measurement, data) {
// Loop through the array of incoming measurements
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const inputMeasurement = data[i];
// Perform calculation and output
// ...
// Output
output(...);
}
}
在计算结束时,一旦为计算的测量构建输出数据后,您应使用输出数据作为参数调用output(),以输出计算的测量。这将通知脚本引擎将您计算出的测量值提取到Senfi中。
output():脚本输出
脚本输出函数是一个预定义的函数调用,无论何时要输出计算的测量,都应调用该函数。
您必须使用有效的测量数据(例如,所有已声明的参数和标签)来调用输出函数以输出计算的测量。请注意,输出测量将自动归因于您在内容管理系统中选择的计算测量名称。该脚本不可能输出另一个计算的测量值。
测试
创建或编辑计算的测量时,可以在内容管理系统中测试计算的测量。
测试数据的格式和值应与输入测量中的实际数据相同。您可以使用单组或多组数据进行测试。
测试数据格式为JSON,使用以下形式的对象数组:
{
"measurement":
"data": []
}
其中measurement是输入测量的名称,而data是来自输入测量的一个或多个测量数据的列表,并遵循着Senfi数据消息的格式。
从测量temperature_v1发送一组测量数据的示例。计算函数的脚本将在测试期间被执行一次:
[
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
"tm_source": xxxxxxxxxx,
"site_id" xxxxxxxx,
"tag1": "xxxxxxxx",
"tag2": "xxxxxxxx",
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
}
]
从测量temperature_v1发送一批三组测量数据的简化示例。计算函数的脚本将在测试期间被执行一次:
[
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
},{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
},{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
}
]
从测量temperature_v1发送三组测量数据的简化示例。计算函数的脚本将在测试期间被执行三次:
[
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
},
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
},
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
}
]
如果您的脚本使用多个输入测量执行计算,则可以指定多个测量。在此示例中,计算函数将执行两次,一次是针对temperature_v1,一次是针对humidity_v1:
[
{
"measurement": "temperature_v1",
"data": [{
...
"temp": xxxxxxxx,
}]
},
{
"measurement": "humidity_v1",
"data": [{
...
"humidity": xxxxxxxx,
}]
}
]
执行
在内容管理系统中创建或编辑计算的测量后,系统将编译您的计算的测量的脚本,并且初始化和调用计算函数:
- 当您完成脚本创建后:初始化函数将会运行
- 当您完成脚本编辑后:初始化函数将会运行
- 当来自每个输入测量的数据到达时:计算函数将会运行。
错误和调试
在脚本初始化或执行期间发生的错误将显示在内容管理系统的开发者选项卡中的调试器中。
您的脚本记录的控制台消息也会显示在调试器中。
例子
示例一:温度刻度转换
此示例显示了计算测量的简单用法。
假设您有一个温度传感器,它以华氏 (℉) 为单位发送原始温度值,而您想以摄氏度 (°C) 为单位显示温度。这将是来自温度传感器的温度测量值输入,其中temperatureF是以℉为单位的温度数据:
{
"tm_source": xxxxxxxxxx,
"site_id" xxxxxxxx,
"tag1": "xxxxxxxx",
"tag2": "xxxxxxxx",
"temperatureF": xxxxxxxxx
}
这是您要输出的计算出的测量值,其中temperatureC是以°C为单位的温度参数。您将保留输入测量的标签,以便将计算的测量正确地归因于原始温度传感器:
{
"tm_source": xxxxxxxxxx,
"site_id" xxxxxxxx,
"tag1": "xxxxxxxx",
"tag2": "xxxxxxxx",
"temperatureC": xxxxxxxxx
}
要将温度测量temperatureF(以℉为单位)转换为temperatureC(以°C为单位),可以使用℉转到°C的公式:
temperatureC = (temperatureF − 32) * 5/9;
由于您只是在数据到达时执行转换,因此无需执行任何初始化任务或声明任何全局变量。因此,您可以将初始化函数留空:
async function init() {
// No initialization tasks required for this simple example
}
将所有代码放在一起,完整脚本将类似于:
/**
* @name: init
* @description: Perform one-time initialization of your script
* param {string}
**/
async function init() {
// No initialization tasks required for this simple example
}
/**
* @name: compute
* @description: Perform computation on input measurements. This function is called when new measurements arrive
* @param {string} measurement - The input measurement name
* @param {Array.<object>} data - The measurement array data
**/
function compute(measurement, data) {
// Loop through the array of incoming measurements,
// and convert 'temperatureF' to 'temperatureC'
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const inputMeasurement = data[i];
const temperatureF = inputMeasurement.temperatureF;
// Calculate the temperature in C
const temperatureC = (temperatureF − 32) * 5/9;
const outputMeasurement = {
tm_source: inputMeasurement.tm_source,
site_id: inputMeasurement.site_id,
tag1: inputMeasurement.tag1,
tag2: inputMeasurement.tag2,
temperatureC: temperatureC,
};
// Output computed measurement
output(outputMeasurement);
}
}
/**
* @function output
* @description: User-invoked function to output a computed measurement
* @param {Object} outputData - Object containing output metrics (required tags, optional tags, measurement metrics)
* @param {string} outputData.tm_source - Timestamp (Same as input measurement)
* @param {string} outputData.site_id - Site Id (Same as input measurement)
* @param {string} outputData.tag1 - Tag1 (Same as input measurement)
* @param {number} outputData.tag2 - Tag2 (Same as input measurement)
* @param {boolean} outputData.temperatureC - Calculated temperature in C
**/
示例二:电梯移动的总楼层数
此示例显示了更复杂的计算测量用法。
假设您有一个会发送楼层位置值的电梯控制器(例如,电梯轿厢位于1楼时,楼层位置值为1;电梯轿厢位于2楼,楼层位置值时为2,等等)。您要使用电梯轿厢位置数据来计算移动的楼层总数。
例如,如果先前报告电梯位于1楼,现在报告电梯位于5楼,则移动的楼层总数为5-1 = 4。如果下一次报告电梯位于第7层,则新移动的总楼层数为(7-5)+ 4 = 6,如此类推。
lift_controller_v1是您输入的电梯控制器的测量(缩写),其中lsid是电梯ID标签,而position是电梯轿厢位置数据:
{
"tm_source": xxxxxxxxxx,
"site_id" xxxxxxxx,
"lsid": "xxxxxxxx",
"position": xxxxxxxxx
}
这是您要输出的计算出的测量值,其中floorsMoved是移动的楼层总数的累积。您将保留输入测量的标签,以正确将计算的测量值归因于原始电梯:
{
"tm_source": xxxxxxxxxx,
"site_id" xxxxxxxx,
"lsid": "xxxxxxxx",
"floorsMoved": xxxxxxxxx
}
由于您要的是累积随时间推移电梯移动的楼层总数,而不仅仅是按单个测量数据执行计算,您将需为此声明一个全局变量totalFloorsMoved:
let totalFloorsMoved;
您的计算函数将跨连续的lift_controller_v1输入测量执行计算。您将声明一个全局变量prevFloors来存储floorsMoved测量的先前值,这样一来,在下一个lift_controller_v1输入测量上执行计算函数时,可以执行以下计算:
let prevFloors;
您还可以使用API函数getStoredValue和setStoredValue将累积值存储到持久性存储中。这样,即便Senfi在系统维护时中终止并重新初始化计算的测量,您也不会丢失累积的数据。
例如,要读取先前计算的总移动楼层,请执行以下操作:
let prevTotalFloorsMoved = await getStoredValue('floorsMoved');
因此,完成的初始化函数将是:
let totalFloorsMoved;
let prevFloor;
/**
* @name: init
* @description: Perform one-time initialization of your script
* param {string}
**/
async function init() {
// Perform initialization of script here
let _totalFloorsMovedVal = await getStoredValue('floorsMoved');
let _prevFloorVal = await getStoredValue('prevFloor');
// Return value from getStoredValue is a JSON string.
// We need to convert it back to the actual values (an integer)
// or null if no value was previously stored
let _totalFloorsMoved = JSON.parse(_totalFloorsMovedVal);
let _prevFloor = JSON.parse(_prevFloorVal);
if (_totalFloorsMoved == null) {
totalFloorsMoved = 0; // This is the first time we run the script. Set to 0
} else {
totalFloorsMoved= _totalFloorsMoved ; // Set to the previously stored value
}
if (_prevFloor == null) {
prevFloor = 0; // This is the first time we run the script. Set to 0
} else {
prevFloor = _prevFloor ; // Set to the previously stored value
}
}
现在我们需要编写计算逻辑:
- 在收到新的批次输入测量时,对于每个单独的测量,请计算自上次测量以来移动的楼层的绝对数量:floors moved = abs(current position - previous position)
- 将移动的绝对楼层数加到移动的累积总数中:total floors moved += floors moved
- 构造并输出计算的测量值
- 将current position存储为previous position,以供下一次迭代
计算函数为:
/**
* @name: compute
* @description: Perform computation on watching measurements. This function is called when new measurements arrive
* @param {string} measurement - The source measurement name
* @param {Array.<object>} data - The measurement array data
**/
function compute(measurement, data) {
// Perform calculation on data here
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const d = data[i];
// On the very first measurement where _prevFloor is 0, set _prevFloor to current position
if (_prevFloor == 0) {
_prevFloor = d.positon;
}
// Calculate the difference in floors moved
const floorsMoved = Math.abs(d.position - _prevFloor) + _totalFloorsMoved;
// Constuct the output measurement
const outputMeasurement = {
site_id: d.site_id,
country: d.country,
lsid: d.lsid,
floorsMoved: floorsMoved
};
// Output computed measurement
output(outputMeasurement );
// Store current values
_prevFloor = d.position;
_totalFloorsMoved = floorsMoved;
}
// Persist global values, to survive script restart
await setStoredValue('floorsMoved', _totalFloorsMoved);
await setStoredValue('prevFloor', _prevFloor);
}
计算的测量脚本API
输出API函数
- output
/**
* @function output
* @description: User-invoked function to output a computed measurement
* @param {object} outputData - Object containing output metrics (required tags, optional tags, measurement metrics)
* @param {string} outputData.lsid - [Example] lsid tag (for lifts)
* @param {string} outputData.country - [Example] country tag
* @param {number} outputData.metric1 - [Example] metric1
* @param {boolean} outputData.metric2 - [Example] metric2
* @param {integer} outputData.metric3 - [Example] metric3
**/
永久存储API函数
- setStoredValue
/**
* @async - Use await to wait for the function to complete
* @function setStoredValue
* @description Persist a value to senfi database. You may retrieve this value using 'getStoreValue'
* @param {string} key
* @param {any} value
**/
- getStoredValue
/**
* @async - Use await to wait for the function to complete
* @function getStoredValue
* @description Retrieve a value previously stored in senfi database.
* @param {string} key
* @return {Promise.<string>} stringified value. Use JSON.parse() to restore the value to original form
**/
计时API函数
- setInterval
/**
* @function setInterval
* @param {function} fn
* @param {integer} interval value, in miliseconds
* @returns {string} token
**/
- clearInterval
/**
* @function clearInterval
* @param {string} token - The return value from setInterval()
**/
- setTimeout
/**
* @function setTimeout
* @param {function} fn
* @param {integer} timeout value, in miliseconds
* @returns {string} token
**/
- clearTimeout
/**
* @function clearTimeout
* @param {string} token - The return value from setTimeout()
**/
记录API函数
以下函数允许您记录消息,而这些消息将显示在内容管理系统开发者选项卡的调试器中。
- console.log
- console.error
- console.warn
- console.info
- console.debug
